Why It Matters to Understand the Different Sources of Energy for Our Future
Understanding the various sources of energy is crucial as we navigate the complexities of our future energy landscape. With the global population surging and the demand for energy increasing, it is imperative to explore not just traditional fossil fuels, but also renewable and alternative energy sources. Each type of energy has distinct advantages and challenges, influencing environmental sustainability, economic stability, and technological advancements. By comprehensively examining these diverse sources of energy, we can make informed decisions that promote a cleaner, more sustainable future.
In this age of environmental awareness and energy transition, recognizing the implications of our energy choices has never been more critical. The shift toward cleaner sources of energy is essential in mitigating the effects of climate change and fostering energy independence. Furthermore, understanding the interplay between different energy sources—and how they can complement one another—will enable us to develop balanced energy strategies. As we delve deeper into the topic, we will uncover how the integration of varied energy sources can lead to a resilient and adaptable energy system, crucial for sustaining both current and future generations.

Overview of Energy Sources: Types and Classifications
Energy is a fundamental component of modern life, and understanding its various sources is essential for sustainable development. The primary types of energy sources can be broadly classified into renewable and non-renewable categories. Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal, are naturally replenished and have a lower environmental impact. These sources are becoming increasingly important as the world shifts towards cleaner energy solutions to combat climate change.
On the other hand, non-renewable energy sources, including fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, are finite resources that have powered industrialization and economic growth for decades. However, their extraction and use contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation. Understanding the implications of these different energy types is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals as they make decisions that will shape a sustainable energy future. The integration of these energy sources into a balanced energy portfolio is vital for meeting the rising global energy demand in a way that prioritizes ecological health and resource conservation.
The Importance of Renewable Energy in Sustainable Development
The transition to renewable energy is imperative for sustainable development in the face of climate change and resource depletion. Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power, offer countless benefits, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions and less reliance on finite fossil fuels. By harnessing these energy sources, we can protect the environment, promote public health, and ensure a more resilient energy infrastructure. This shift is not only an ecological necessity but also an economic opportunity, fostering job creation in emerging green technologies and industries.
Furthermore, embracing renewable energy plays a crucial role in energy security and independence. As countries strive to reduce their vulnerability to fluctuating fossil fuel markets, developing local renewable resources provides a sustainable path forward. This not only enhances energy access for underserved communities but also supports global efforts to mitigate climate change. By investing in and understanding renewable energy, we can take significant strides towards a more sustainable future, ensuring that generations to come have access to clean, reliable, and affordable energy.
Why It Matters to Understand the Different Sources of Energy for Our Future - The Importance of Renewable Energy in Sustainable Development
| Energy Source | Percentage of Global Energy Consumption (%) | Carbon Emissions (gCO2/kWh) | Sustainability Rating (1-10) | Potential for Growth (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Energy | 3.5 | 0 | 9 | 30 |
| Wind Energy | 7.3 | 12 | 8 | 25 |
| Hydropower | 16.2 | 8 | 7 | 5 |
| Geothermal Energy | 0.4 | 4 | 8 | 15 |
| Biomass Energy | 10.0 | 70 | 6 | 20 |
Fossil Fuels: Pros, Cons, and Environmental Impact
Fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and natural gas, have been the backbone of the global energy supply for over a century. One of their primary advantages is their high energy density, which allows for the efficient generation of electricity and powering various modes of transportation. Additionally, fossil fuel infrastructure is already well-established, making it relatively inexpensive to continue utilizing these resources in the short term. This accessibility has contributed to economic growth in many regions, providing jobs and supporting industries that rely on fossil fuel extraction and consumption.
However, the reliance on fossil fuels comes with significant downsides, particularly in terms of environmental impact. The burning of fossil fuels releases large amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change and air pollution. This environmental degradation can lead to severe consequences, including extreme weather events, habitat destruction, and health problems in affected populations. Furthermore, the extraction processes can be disruptive, causing ecological damage and threatening biodiversity. As the world grapples with the urgent need for sustainable energy solutions, understanding the pros and cons of fossil fuels becomes essential in navigating the transition to renewable energy sources that minimize environmental harm.
Energy Sources: Pros and Cons
This chart illustrates the pros and cons of various energy sources, highlighting their environmental impact and overall viability for a sustainable future. The data reflects the general insights regarding fossil fuels, renewable energy, and nuclear power.
Emerging Technologies in Energy Generation and Storage
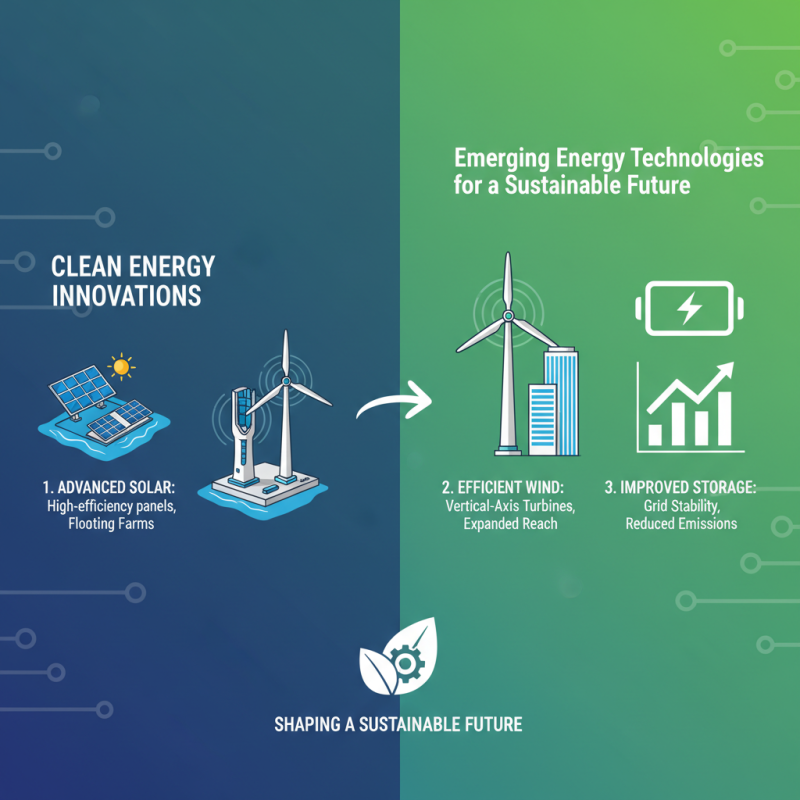
Emerging technologies in energy generation and storage play a crucial role in shaping a sustainable future. One of the most promising advancements is the development of advanced solar panels and wind turbines, which harness renewable energy more efficiently than ever before. These technologies not only increase the amount of energy generated from natural sources but also contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Innovations such as floating solar farms and vertical-axis wind turbines are making it possible to utilize areas that were previously unsuitable for traditional energy infrastructure, thereby expanding the reach of renewable resources.
In addition to generation, energy storage technologies are experiencing significant breakthroughs. Battery technologies, particularly those using solid-state and lithium-sulfur chemistries, are increasing energy density and reducing costs, thus enabling longer storage durations and better performance. This capability is essential for balancing supply and demand, especially with intermittent sources of energy like solar and wind. Moreover, advancements in grid-scale storage solutions, such as pumped hydro and compressed air energy storage, are enhancing the resilience and reliability of our energy systems. Together, these emerging technologies are paving the way for a cleaner, more efficient energy landscape that is essential for sustainable development.
The Role of Energy Policy in Shaping Our Energy Future
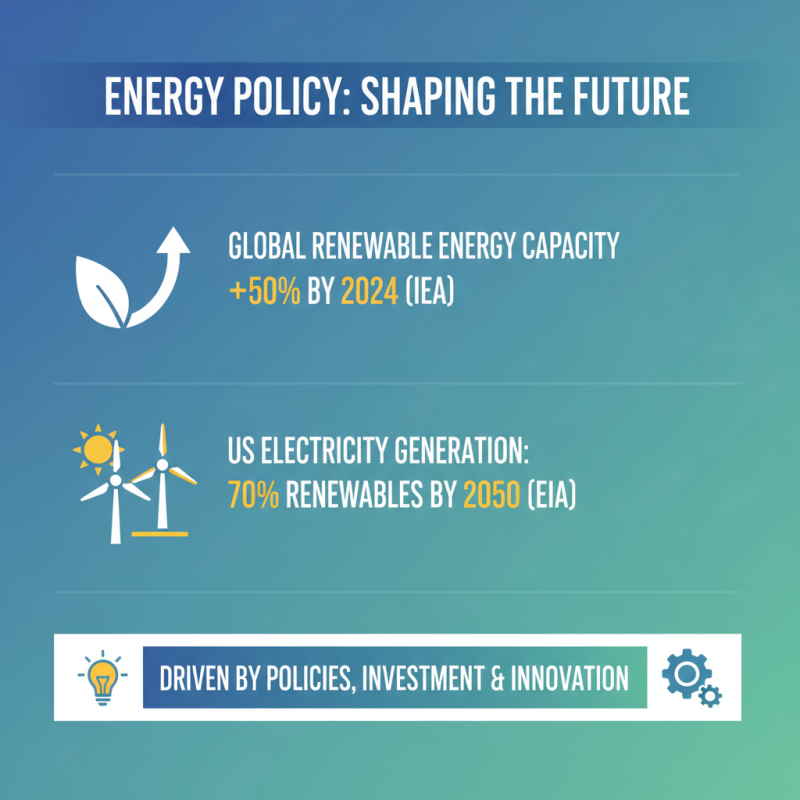
Energy policy plays a crucial role in shaping the future of energy production and consumption, influencing everything from investment in renewable technologies to regulations on fossil fuels. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global renewable energy capacity is expected to grow by 50% between 2019 and 2024, driven by supportive policies and investments. Policymakers are tasked with creating frameworks that facilitate this transition, ensuring that clean energy sources can compete with traditional energy systems. For instance, the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) projects that by 2050, renewable sources could account for 70% of total electricity generation, driven by policies that encourage innovation and infrastructure development.
Furthermore, effective energy policy not only supports environmental goals but also aims to enhance energy security and economic stability. The World Bank highlights that countries actively investing in renewable initiatives can decrease their dependence on imported fossil fuels, thereby insulating themselves from price volatility. By promoting a diversified energy mix, nations can create resilient economies capable of withstanding global energy supply shocks. In essence, the energy policy framework will determine whether countries can leverage technological advancements to create sustainable energy systems that support long-term growth and environmental protection.
Related Posts
-

Exploring Alternative Energy Innovations at the 138th Canton Fair 2025: A Data-Driven Insight
-

Unlocking the Future: Innovative Energy Solutions and Sustainable Sources for Tomorrow
-

The Future of Sustainable Living Exploring the Innovations in Re Energy Solutions
-

Top 10 Sources of Energy: Which Are the Most Sustainable and Efficient?
-

Top 10 Benefits of Alternative Energy for a Sustainable Future
-

Top 10 Energy Sources for Sustainable Energy: What You Need to Know

