Top 10 Sources of Energy: Which Are the Most Sustainable and Efficient?
In the quest for a sustainable future, understanding the various sources of energy is paramount. As the world grapples with the implications of climate change and energy security, experts in the field have emphasized the need for a strategic approach to energy sourcing. Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned energy policy analyst, aptly states, "The transition to cleaner sources of energy is not just an environmental necessity, but an economic opportunity that can drive innovation and job creation." This sentiment resonates deeply as we explore the top ten sources of energy, assessing their sustainability and efficiency in meeting the world's growing energy demands.
As we delve into this critical topic, it is essential to evaluate each source not only on its current viability but also on its long-term potential. Renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, and hydroelectric, are at the forefront of this discussion, promising both lower environmental impact and greater energy independence. Conversely, traditional fossil fuels remain a significant part of the energy mix, prompting ongoing debates about their sustainability. By analyzing the benefits and drawbacks of each energy source, we can gain valuable insights into how best to navigate the transition toward a more sustainable energy landscape for future generations.

Top 10 Energy Sources: An Overview of Sustainability and Efficiency
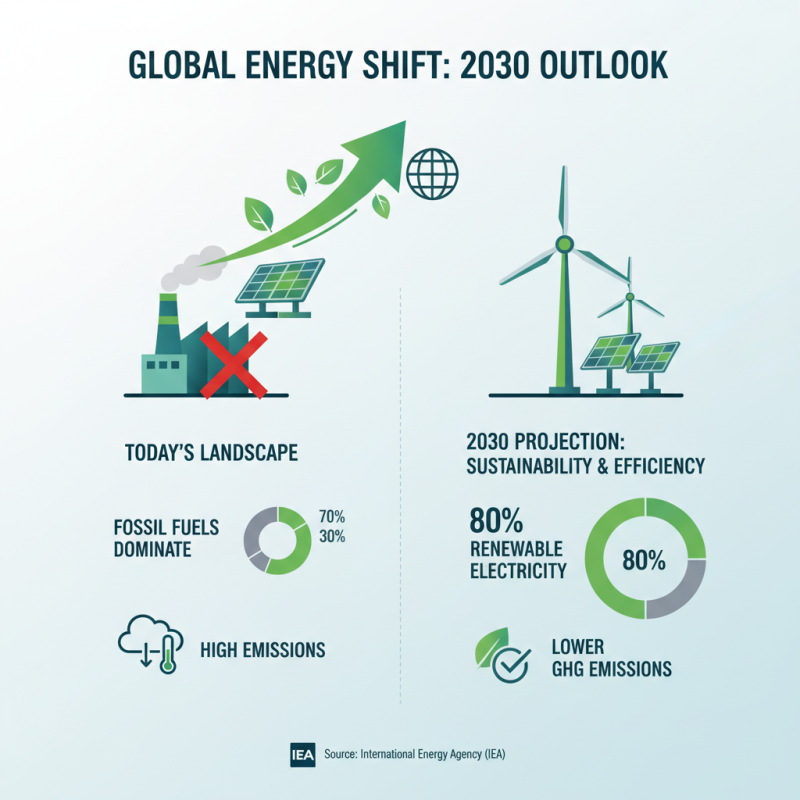
The global energy landscape is rapidly evolving, with an increasing emphasis on sustainability and efficiency. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, are set to dominate future energy production, potentially accounting for 80% of global electricity generation by 2030. Such a shift not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also lowers greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a more sustainable energy framework.
In contrast, traditional energy sources like coal and oil, while historically significant, are facing mounting pressures. A report from the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) indicates that transitioning to cleaner alternatives could save $12 trillion globally in health and environmental costs by 2040. Furthermore, energy efficiency measures can reduce energy consumption by up to 30% without sacrificing economic growth, highlighting the necessity of integrating sustainable practices across various sectors. As industries pivot towards these innovative energy solutions, understanding their sustainability and efficiency metrics will be crucial for policymakers and stakeholders alike.
Evaluating Renewable Energy: Solar, Wind, and Hydro Potential
Renewable energy sources are increasingly recognized for their sustainability and efficiency, especially in specific geographic contexts. In Sudan, hydropower is a dominant contributor, accounting for 54.6% of the country’s electricity grid. This highlights the potential of hydro energy in regions with abundant water resources. Conversely, other renewable sources like biomass and solar energy are significantly underutilized, demonstrating a gap in development that could potentially be addressed through strategic investments and policy changes.
In contrast to Sudan, the situation in Iran showcases a broader potential for diverse renewable energy options. A comprehensive assessment using a multi-criteria decision-making approach reveals the urgent need for the country to harness its rich resources, possibly suggesting a pathway for hybrid systems that integrate various renewable technologies. This is in line with global trends emphasizing the importance of a diversified energy portfolio to enhance energy security and sustainability. As nations like Iran evaluate their renewable capabilities, the imperative of deploying effective technologies becomes increasingly critical in the global pursuit of renewable energy solutions.
Fossil Fuels: Current Usage Statistics and Environmental Impact
Fossil fuels remain the dominant source of energy across the globe, powering industries, transportation, and homes. According to recent statistics, they account for approximately 80% of the world's energy consumption. Despite their widespread use, fossil fuels come with severe environmental consequences. The extraction and burning of coal, oil, and natural gas release significant amounts of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change and global warming.
Moreover, the environmental impact extends beyond carbon emissions. The processes involved in fossil fuel extraction, including drilling and mining, can lead to habitat destruction, oil spills, and water contamination. These effects not only harm local ecosystems but also pose risks to public health, particularly in communities situated near fossil fuel operations. As awareness of these issues grows, there is an increased push towards transitioning to more sustainable energy sources that mitigate environmental damage while providing efficient alternatives.
Top 10 Sources of Energy: Which Are the Most Sustainable and Efficient?
| Energy Source | Usage (%) | Sustainability Score (1-10) | Environmental Impact (CO2 Emissions, g/kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Gas | 40 | 6 | 450 |
| Coal | 27 | 3 | 900 |
| Oil | 33 | 4 | 800 |
| Nuclear | 10 | 8 | 10 |
| Hydroelectric | 16 | 9 | 2 |
| Solar | 11 | 10 | 20 |
| Wind | 8 | 10 | 15 |
| Geothermal | 4 | 8 | 10 |
| Biomass | 2 | 5 | 200 |
| Tidal | <1 | 9 | 0 |
Nuclear Energy: The Balance of Safety, Waste, and Efficiency
Nuclear energy is often celebrated for its potential to provide vast amounts of power with minimal greenhouse gas emissions. Recent advancements in nuclear technology have made significant strides toward improving both safety and efficiency. A breakthrough in China highlights the global potential for clean energy, demonstrating innovative methods for managing radioactive waste. These new thermal treatment processes, such as vitrification, allow for safer storage and disposal of nuclear waste, addressing one of the major concerns surrounding this power source.
Tips: When considering nuclear energy, it's essential to stay informed about the latest technologies and their implications for safety. Engage with news and research to understand how advancements can impact energy policy and environmental sustainability. Additionally, exploring the balance between efficiency and safety in reactor design can provide insight into the future of nuclear energy.
The debate surrounding nuclear waste recycling is another crucial aspect. As the industry evolves, finding ways to recycle and manage waste can mitigate environmental concerns while maximizing energy efficiency. Innovations in Generation IV reactor technology promise to enhance the overall safety profile of nuclear energy, paving the way for a more sustainable energy future. Engaging with these discussions can help illuminate the complexities of nuclear energy and its role in achieving clean energy goals.
Emerging Technologies: Biofuels and Geothermal Energy Advances
Emerging technologies in renewable energy, particularly biofuels and geothermal advantages, are gaining traction as pivotal components of the energy transition. The McKinsey Global Institute has highlighted that while some challenges in the energy sector are being addressed, tougher obstacles remain. More efficient biofuel production methods are essential as they promise to reduce greenhouse gas emissions significantly. For instance, advancements in second-generation biofuels, derived from non-food biomass, can lead to a carbon intensity reduction of up to 85% compared to conventional fossil fuels.
Geothermal energy also presents compelling opportunities. Recent developments in enhanced geothermal systems can provide substantial power generation capacity. Currently, the U.S. geothermal power generation profile showcases a potential growth to 163 gigawatts, positioning it as a viable alternative to fossil fuels. Moreover, strategic partnerships, such as those sought by Italy's climate envoy with the U.S. on nuclear and clean energy, emphasize the global push towards sustainable energy solutions. As these technologies evolve, they not only promise enhanced efficiency but also a cleaner, more resilient energy future.
Related Posts
-

Exploring Alternative Energy Innovations at the 138th Canton Fair 2025: A Data-Driven Insight
-

Exploring Sustainable Energy Innovations at 2025 China 138th Canton Fair
-

What is Energy Solutions and How They Impact Global Sustainability Efforts
-

Revolutionizing Energy Solutions: Innovative Approaches for a Sustainable Future
-

Unlocking the Future: How Alternative Energy Solutions Can Power a Sustainable Tomorrow
-

Unlocking the Future: Innovative Energy Solutions and Sustainable Sources for Tomorrow

