Technology and Energy Tips for Sustainable Solutions?
In today's world, technology and energy are intertwined like never before. As we strive for sustainable solutions, the choices we make matter. Each step can lead us closer to a greener planet. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind harness the potential of nature. Innovative technologies support these efforts and make them more efficient.
Cities, for example, are increasingly using smart technology. Smart grids help manage energy use better. However, reliance on technology can also raise questions. Are we truly making the best choices for sustainability? Sometimes, the latest gadgets produce more waste than benefit. Reflection is needed.
Investing in energy-efficient appliances is another way to contribute. Simple changes can reduce demand on our energy resources. But, is it enough? The path to sustainable living is not perfect. There are challenges ahead. By critically examining our use of technology and energy, we can find solutions that truly benefit both the environment and ourselves.
Innovative Technological Solutions for Sustainable Energy Production
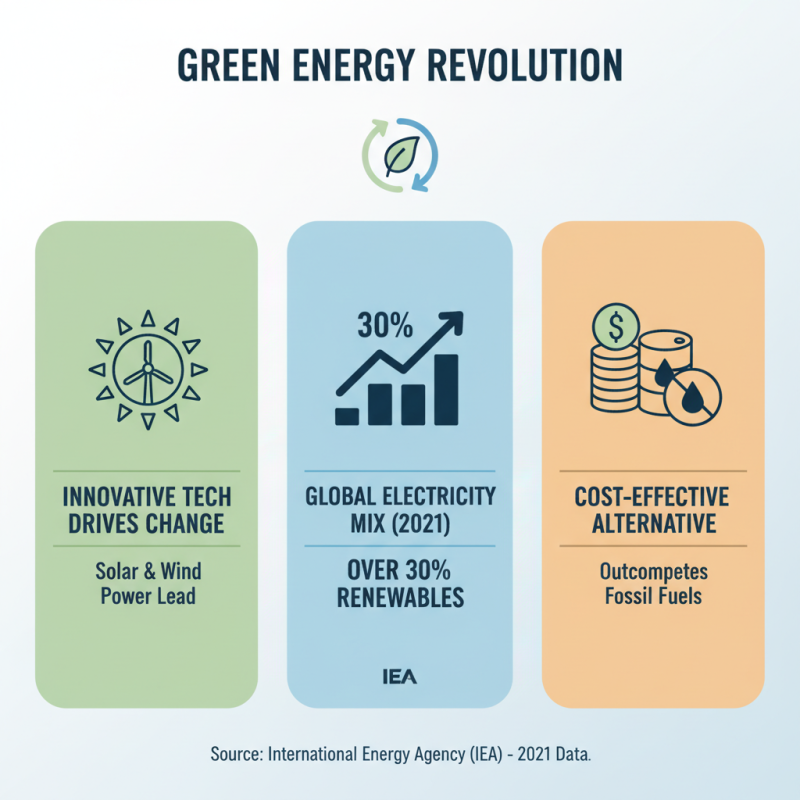
Innovative technologies are transforming sustainable energy production. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewables contributed to over 30% of global electricity generation in 2021. This shift reflects the potential of green energy sources like solar and wind power. Increasingly, these sources are becoming cost-effective alternatives to traditional fossil fuels.
The use of smart grids is a notable advancement. With digital technology, energy distribution becomes more efficient. A report from the World Economic Forum highlights that smart grids can reduce energy loss by up to 30%. However, the challenges remain. Many regions lack the infrastructure for these technologies. Investment in advanced energy storage solutions is crucial. They can help balance supply and demand effectively.
Still, not every innovation leads to immediate success. Many pilot projects do not scale as expected. Data shows a significant dropout rate for wind energy installations due to high initial costs. This realization prompts a critical examination of funding and policy support for new technologies. The focus must shift to reliable and scalable solutions for wider adoption.
Energy Efficiency: Smart Technologies for Reducing Consumption
Smart technologies play a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency. According to the International Energy Agency, buildings account for approximately 40% of global energy consumption. Implementing smart systems can help significantly reduce this figure. For example, smart thermostats automatically adjust temperatures based on occupancy. This eliminates energy waste.
Real-time monitoring can also make a difference. The U.S. Department of Energy found that energy management systems can lower energy use by 10-30%. These systems track usage patterns and identify inefficiencies. Surprisingly, many facilities are still unaware of their potential savings.
Adopting renewable energy sources is vital. A report from the World Resources Institute indicates that solar energy installations can cut emissions by 90%. Many communities lag in embracing this trend. Awareness campaigns could bridge this gap. The transition to smart technologies is not always smooth. Traditional mindsets can hinder progress. Education is needed to maximize the potential of energy-efficient solutions.
Technology and Energy Tips for Sustainable Solutions - Energy Efficiency: Smart Technologies for Reducing Consumption
| Technology | Description | Energy Savings (%) | Implementation Cost ($) | Payback Period (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Thermostats | Automated temperature control to optimize heating and cooling. | 15-20% | 200 | 1-2 |
| LED Lighting | Energy-efficient lighting solution with longer lifespan. | 75-80% | 50 | 0.5-1 |
| Energy Monitoring Systems | Track and manage energy use in real-time. | 10-15% | 300 | 2-3 |
| High-Efficiency HVAC Systems | Advanced systems that consume less energy while maintaining comfort. | 20-30% | 5000 | 5-7 |
| Smart Appliances | Connected devices that optimize usage based on energy demands. | 10-25% | 800 | 3-4 |
Renewable Energy Sources: Harnessing Nature for Sustainable Solutions
In the quest for sustainable energy, renewable sources have become vital. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy capacity surged by 260 gigawatts in 2020 alone. This growth showcases how wind, solar, and hydropower are transforming our energy landscape.
Solar energy, for instance, is harnessed from sunlight and converted into electricity. In sunny regions, solar panels can provide a significant portion of energy needs.
Wind energy takes advantage of natural wind patterns to generate power. The Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC) reported that wind energy produced over 700 terawatt-hours in 2020. This was a critical year for renewables, reflecting a potential for job creation and energy independence. However, challenges exist. The variability of renewable sources leads to fluctuations in energy supply. Storage solutions and grid management must improve to address these inconsistencies.
Hydropower remains the largest renewable energy source. It generates about 16% of the world’s electricity, according to the World Nuclear Association. While it harnesses the power of flowing water, large dams can disrupt local ecosystems. Balancing energy needs with environmental impact is essential. As we venture toward a sustainable future, a holistic approach to energy systems is needed.
Smart Grids: Enhancing Energy Distribution and Management
Smart grids represent a transformative shift in energy distribution and management. They incorporate advanced technology to optimize the flow of electricity. By 2025, the smart grid market is projected to reach $61 billion, reflecting a growing commitment to sustainable energy solutions. These networks utilize sensors, meters, and data analytics to enhance efficiency and reduce waste.
Energy loss in traditional systems can reach 8-15%. Smart grids help lower this figure significantly. They enable real-time monitoring of energy use. This means better demand-response strategies can be implemented. Consumer engagement is vital. Users receive instant feedback on their energy consumption patterns, encouraging more responsible usage. Yet, many people still struggle to change their habits.
Despite the advances, challenges remain. Cybersecurity threats pose a considerable risk to smart grid integrity. Additionally, the initial investment for infrastructure upgrades can deter smaller utilities. Underlying issues like regulatory hurdles also complicate the transition. There is a need for ongoing dialogue among stakeholders to foster collaboration. The path to fully realizing the potential of smart grids requires continuous improvement and reflective practices.
Smart Grids: Enhancing Energy Distribution and Management
This chart demonstrates the average energy distribution among different sectors influenced by smart grid technology over the past five years. The data illustrates how smart grids optimize energy delivery and promote sustainability in various areas.
Energy Storage Technologies: Key to a Sustainable Future
Energy storage technologies play a vital role in building a sustainable future. They allow us to store excess energy generated from renewable sources. For example, solar panels produce energy during daylight. However, the demand for energy does not always align with production.
Batteries, pumped hydro, and flywheels are common storage solutions. Each has unique benefits and challenges. Batteries can be used at home and tailored for specific needs. Yet, their lifespan and recycling processes require improvement. Pumped hydro is reliable but depends on geographical features. Flywheels are efficient but often require a higher initial investment.
Innovative approaches are being tested. For instance, research explores using less common materials. While promising, these alternatives raise questions about efficiency and scalability. Technology must advance to reduce costs and environmental impact. This ongoing journey demands collaboration and commitment. It’s essential to reflect on our progress as we push towards sustainable solutions.
Related Posts
-

Harnessing Power Energy for a Sustainable Future The Role of Renewable Sources in Global Energy Consumption
-

Innovative Energy Solutions: Transforming Sustainability for a Greener Future
-

Unlocking the Future: How Power Energy Innovations are Shaping Our Sustainable World
-

2025 Top Technology and Energy Innovations That Will Change Our Future
-

Harnessing Smart Grid Energy Innovations at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Exploring Sustainable Energy Innovations at 2025 China 138th Canton Fair

