How to Optimize Smart Grid Energy Solutions in 2026?
As we approach 2026, the importance of optimizing smart grid energy solutions cannot be overstated. Experts like Dr. Laura Evans, a leading authority in energy systems, emphasize, "Efficient energy management will redefine our approach to smart grid technology." The evolving landscape of smart grid energy is marked by new challenges and opportunities.
The quest for sustainability demands innovative methods to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. The integration of renewable sources is crucial. However, many systems still struggle with outdated infrastructure. There’s a clear need for modernized solutions that can adapt to changing energy demands.
Moreover, user engagement in smart grid energy is still lacking. Educating consumers about their role can lead to greater energy savings. Yet, there is often a disconnect between the technology and the public’s understanding. Striking a balance remains a challenge. Addressing these issues requires careful reflection and continued dialogue among stakeholders.
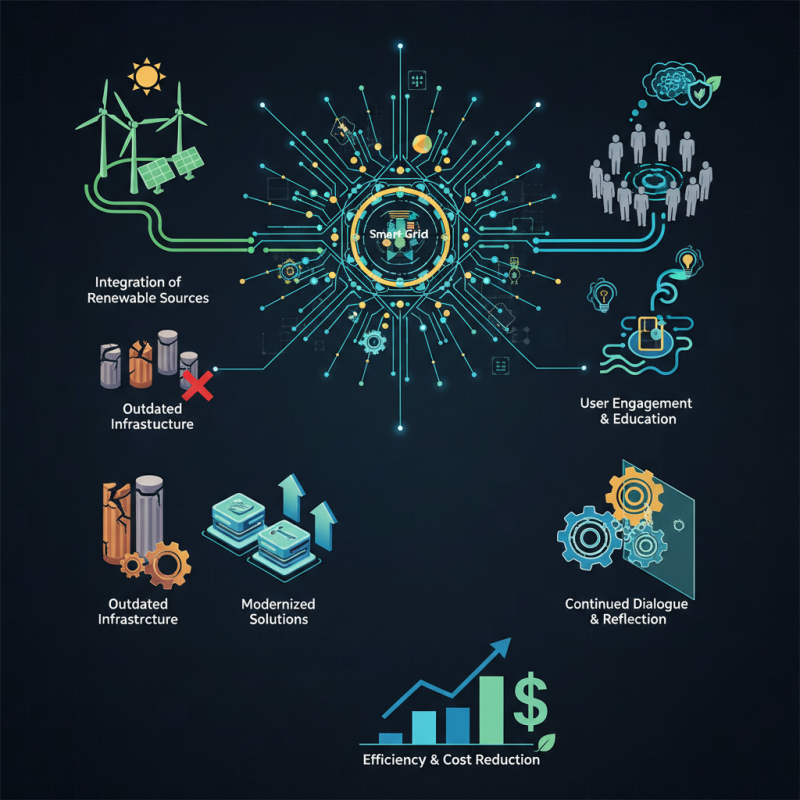
Strategies for Enhancing Smart Grid Infrastructure Efficiency
Smart grid infrastructure is crucial for efficient energy solutions. Enhancing communication technology can significantly improve grid operations. However, many utilities still rely on outdated systems. Upgrading to advanced sensors and IoT devices can lead to real-time monitoring. This allows for faster response to outages and energy demand fluctuations.
Investments in renewable energy sources must also be considered. Incorporating solar and wind energy into the grid can reduce dependency on fossil fuels. Yet, challenges remain in energy storage solutions. Current battery technology may not suffice for large-scale implementation. Addressing this gap requires innovation and collaboration among various sectors.
Moreover, training the workforce is essential. Many employees lack the skills to operate advanced smart grid systems. Ongoing education and awareness programs can help bridge this gap. Nonetheless, driving widespread adoption remains a challenge. Stakeholder engagement is often inconsistent, leading to missed opportunities for improvement. Balancing technology and community needs is a complex journey that requires careful navigation.
Integrating Renewable Energy Sources into Smart Grid Systems
The integration of renewable energy sources into smart grid systems is crucial for optimizing energy solutions. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy sources accounted for about 29% of global electricity generation in 2022. This number is expected to rise as more regions invest in clean technologies. However, challenges persist in storage and grid reliability.
Smart grids must handle variability from sources like solar and wind. Reports indicate that battery storage capacity needs to increase significantly. Currently, about 200 GWh are installed worldwide, but experts suggest a target of 1,000 GWh by 2030. Achieving this goal will enhance grid stability, ensuring that energy supply matches fluctuating demand. The intersection of reliable storage and real-time data will guide energy distribution effectively.
Inefficiencies exist, though. Many grid systems still rely on aging infrastructure. A concerted push towards modernizing these systems is essential. As noted in recent surveys, nearly 30% of energy professionals feel that outdated technology hinders renewable integration. A disconnect between innovation and existing frameworks poses a barrier. Without reflection and strategic upgrades, the full potential of renewable integration may remain untapped.
How to Optimize Smart Grid Energy Solutions in 2026? - Integrating Renewable Energy Sources into Smart Grid Systems
| Dimension | Indicator | Data (2026) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Integration | Percentage of Grid Energy from Renewables | 65% | National Energy Agency |
| Smart Meter Deployment | Number of Smart Meters Installed | 75 million | Market Research Reports |
| Energy Storage Solutions | MW Capacity of Storage Systems | 50,000 MW | Global Energy Consortium |
| Demand Response Programs | Number of Participating Customers | 25 million | Utility Reports |
| Carbon Emissions Reduction | Reduction in CO2 Emissions (Million Tons) | 200 million tons | Environmental Studies |
Advanced Energy Storage Solutions for Smart Grid Optimization
Advanced energy storage solutions are critical for optimizing smart grids in 2026. With the global energy storage market projected to reach $546 billion by 2035, advancements in battery technologies are more important than ever. The use of lithium-ion batteries, currently holding 73% of the market share, needs to be scrutinized. While they are efficient, their reliance on scarce materials raises sustainability concerns. Alternatives like solid-state batteries could offer better performance and safety.
Investments in advanced storage systems can enhance grid resilience. According to a report by the U.S. Department of Energy, up to 45% of renewable energy can be stored effective. However, challenges remain in integrating these systems. Many utilities still lack the infrastructure for efficient energy distribution. Studies show storage solutions can reduce energy costs by 30%. But the true optimization of smart grids requires a comprehensive approach, including regulatory support and consumer engagement.
As technology evolves, more focus on cost-effective solutions will be necessary. For instance, flow batteries and compressed air energy storage present opportunities but haven't been widely adopted. Failures in pilot projects highlight the need for tailored approaches. Building a smarter grid involves learning from these experiences and adopting flexible energy models. The path to 2026 will not be easy.
Utilizing Data Analytics for Smart Grid Performance Improvement

In 2026, smart grid optimization will rely heavily on data analytics. By analyzing vast amounts of energy data, utilities can identify inefficiencies. This approach allows for precise adjustments in energy distribution. Using algorithms, they can predict energy demand with greater accuracy. This will help in reducing wastage and improving overall grid performance.
Tips: Focus on real-time data processing. It helps in uncovering patterns faster. Implement machine learning models to forecast energy needs. This can lead to better resource allocation during peak hours.
However, it’s crucial to address data privacy concerns. Striking a balance between analytics and user privacy is challenging. Many consumers may feel uneasy about their data being used. Transparency in data usage can help build trust. Engaging with the community fosters confidence in smart grid initiatives.
Implementing Cybersecurity Measures in Smart Grid Technologies
As we approach 2026, optimizing smart grid energy solutions becomes crucial for future sustainability. One key aspect is cybersecurity. A report by the U.S. Department of Energy found that 70% of utilities experienced some form of cyber attack in the past year. This alarming statistic highlights the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
Implementing strong cybersecurity frameworks can reduce vulnerabilities. Regularly updating software is essential. In fact, 61% of breaches involve unpatched software. Ensuring all systems are updated can mitigate risks significantly. Furthermore, creating a culture of cybersecurity awareness among staff could be key. Employee training programs can empower personnel to recognize and respond to threats effectively.
Tips: Focus on creating firewalls and intrusion detection systems. These tools help monitor and protect against unauthorized access. Consider using multi-factor authentication for critical systems. This adds an extra layer of security against potential breaches.
Investing in cybersecurity is not just about protection; it’s about ensuring reliability and trust in smart grid technologies. Industry reports indicate that utilities spending on cybersecurity is expected to grow by over 20% annually. It reflects a growing understanding that strong defenses are fundamental to operational success.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Innovative Solutions for Energy Efficiency You Need to Know
-

Harnessing Smart Grid Energy Innovations at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Wind Farm Energy Innovations at 2025 China Import and Export Fair: Harnessing a $1 Trillion Industry
-

What is Energy Solutions and How They Impact Global Sustainability Efforts
-

Revolutionizing Energy Solutions: Innovative Approaches for a Sustainable Future
-

Harnessing Power Energy for a Sustainable Future The Role of Renewable Sources in Global Energy Consumption

