Top 5 Innovations in Electrical Engineering Transforming Solar Energy Systems
The landscape of renewable energy is rapidly evolving, and electrical engineering plays a pivotal role in the transformation of solar energy systems. As innovations emerge, they redefine how we harness, convert, and utilize solar power. One notable expert in the field, Dr. Emily Torres, a leading researcher in electrical engineering solar energy, highlights this exciting shift by stating, "The future of solar energy hinges on our capacity to innovate within electrical engineering, leading to efficient and sustainable solutions."
In 2025, the integration of cutting-edge technologies—such as enhanced photovoltaic materials, advanced energy storage systems, and intelligent grid management—will significantly enhance the efficiency and accessibility of solar energy systems. These advancements not only promise to lower costs but also to increase energy output in various applications, from residential to industrial. As Dr. Torres emphasizes, the intersection of electrical engineering and solar energy is where we will see the most impactful developments, enabling cleaner energy solutions to meet the growing global demand.
This exploration into the top five innovations shaping the future of electrical engineering solar energy systems illustrates the dynamic interplay between technology and sustainability. By embracing these advancements, we can expect to see a paradigm shift in how we generate and consume solar energy, ultimately paving the way for a more sustainable future.

Innovative Photovoltaic Materials Revolutionizing Solar Cell Efficiency
The advancement of photovoltaic materials is at the forefront of innovations transforming solar energy systems. The emergence of perovskite solar cells has garnered significant attention in recent years. These materials, characterized by their unique crystal structure, showcase remarkable efficiency rates, surpassing traditional silicon-based cells. By optimizing light absorption and charge carrier mobility, perovskite cells can achieve energy conversion efficiencies beyond 25%, driving the pursuit of more sustainable energy solutions.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring tandem solar cells, which combine different photovoltaic materials to maximize energy output. These multi-junction systems utilize both perovskite and silicon layers, enhancing overall performance and efficiency. The integration of organic photovoltaics also holds promise, offering lightweight and flexible alternatives for diverse applications. As these innovative materials continue to evolve, the potential for solar energy systems to provide cleaner, more efficient power expands, paving the way for a greener future.
Top 5 Innovations in Electrical Engineering Transforming Solar Energy Systems
Advanced Energy Storage Solutions Enhancing Solar Power Reliability
In recent years, advancements in energy storage solutions have played a pivotal role in enhancing the reliability of solar power systems. These innovations not only improve the efficiency of solar energy utilization but also address one of the biggest challenges—intermittency. Advanced battery technologies, such as lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, are now capable of storing significant amounts of energy, allowing users to harness solar power even during cloudy days or at night. This transformation enables a more consistent and dependable energy supply, making solar energy a viable option for both residential and commercial applications.
Another noteworthy innovation is the integration of smart technology into energy storage systems. These technologies not only optimize the charging and discharging processes but also enable remote monitoring and management. Users can now track their energy consumption patterns and make adjustments in real-time, maximizing the effectiveness of their solar power systems. This level of control greatly enhances the reliability of solar energy, ensuring that it meets the specific needs of users regardless of external conditions.
Smart Grid Technologies Integrating Solar Energy into National Networks
The integration of solar energy into national networks has seen significant advancements with the rise of smart grid technologies. These innovations enable efficient energy distribution, allowing for real-time monitoring and management of power resources. Smart grids facilitate better communication between energy providers and consumers, leading to optimized energy usage and reduced operational costs. Additionally, they empower users with tools to harness solar energy effectively, whether through residential solar panels or larger solar farms.
One of the most crucial aspects of smart grid technologies is their ability to balance supply and demand in dynamic environments. By utilizing advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence, these systems can predict energy consumption patterns and adjust the integration of solar energy accordingly. This not only enhances the reliability of energy supply but also supports the growth of renewable energy sources, significantly contributing to sustainability goals. As these smart grids continue to evolve, their role in mainstreaming solar energy into the national network becomes increasingly vital, paving the way for a greener and more resilient energy future.
Power Electronics Innovations Optimizing Solar Inverter Performance
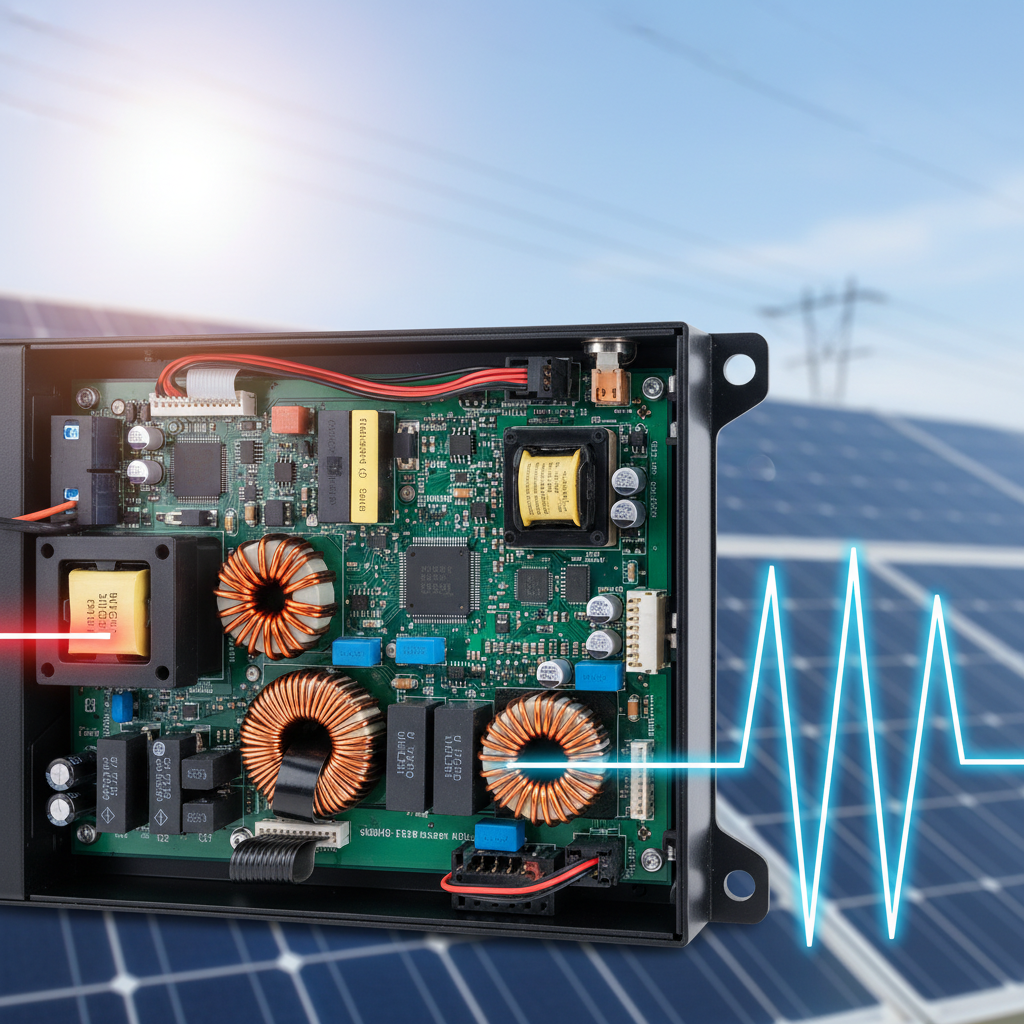
Power electronics have become crucial in optimizing the performance of solar inverters, which are essential for converting the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) usable by the electrical grid. Recent innovations in power electronics technology are significantly improving inverter efficiency and functionality. Advanced control algorithms and digital signal processing techniques allow for better real-time monitoring and management of solar energy conversion, leading to reduced energy losses and enhanced output stability.
Another important trend is the integration of wide-bandgap semiconductors, such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN), into inverter designs. These materials operate at higher voltages and temperatures than traditional silicon-based components, resulting in smaller, lighter, and more efficient inverters. This not only boosts the overall system performance but also reduces the cost of solar installations, making renewable energy more accessible. As these innovations continue to evolve, they promise to unlock the full potential of solar energy systems, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
IoT and AI Applications in Solar Energy System Monitoring and Management
The integration of IoT and AI in solar energy systems is revolutionizing how these systems are monitored and managed. IoT devices, such as smart sensors and connected photovoltaic modules, provide real-time data on energy production, weather conditions, and system performance. This abundant flow of information allows for immediate analysis and rapid decision-making. For instance, predictive maintenance is now possible, where data analytics can anticipate failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
AI-powered algorithms enhance these functionalities further by analyzing historical data patterns and optimizing energy output. Machine learning models can adjust system parameters based on changing environmental conditions, leading to improved efficiency and energy reliability. Additionally, AI can facilitate demand response strategies, enabling solar energy systems to communicate dynamically with the grid, ensuring that energy supply matches consumption patterns. Through these advanced technologies, the management of solar energy systems becomes smarter, more efficient, and ultimately more sustainable.
Top 5 Innovations in Electrical Engineering Transforming Solar Energy Systems
| Innovation | Description | Key Benefits | Application Areas | Current Trends |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoT Sensors | Integration of IoT sensors to collect real-time data from solar panels. | Improved efficiency and proactive maintenance. | Residential and commercial solar installations. | Rising adoption in smart homes. |
| AI Optimization | Utilizing AI algorithms to optimize energy generation based on weather forecasts. | Maximized output and reduced costs. | Utility-scale solar farms. | Growing demand in large-scale energy projects. |
| Predictive Analytics | Analyzing data trends to predict maintenance needs and system performance. | Reduced downtime through timely interventions. | Maintenance management for solar farms. | Evaluation of energy asset lifecycles. |
| Smart Inverters | Advanced inverters that adjust power output based on grid demands. | Enhanced grid stability and integration. | Grid-tied solar systems. | Increased grid resilience during peak loads. |
| Blockchain Technology | Utilizing blockchain for secure energy trading and transaction transparency. | Increased trust and reduced transaction costs. | Peer-to-peer energy trading platforms. | Emerging use in decentralized energy markets. |
Related Posts
-

Wind Farm Energy Innovations at 2025 China Import and Export Fair: Harnessing a $1 Trillion Industry
-

Revolutionizing Energy Solutions: Innovative Approaches for a Sustainable Future
-

Top 10 Innovative Solutions for Energy Efficiency You Need to Know
-

Exploring Alternative Energy Innovations at the 138th Canton Fair 2025: A Data-Driven Insight
-

Harnessing Wind Power Energy for a Sustainable Future in Innovative Technologies
-

Unlocking Efficiency: Innovative Strategies for Project Management in the Energy Sector

