Why is Energy Important and What are its Sources?
Energy plays a crucial role in our daily lives. As Dr. Fiona Reynolds, an expert in renewable energy, states, "Understanding energy and sources of energy is key to a sustainable future." This highlights the importance of recognizing various energy types and their origins.
We rely on energy for countless activities, from heating our homes to powering our devices. The sources of energy are diverse, including fossil fuels, solar power, wind, and hydropower. Each source has its pros and cons. For instance, fossil fuels are abundant but harmful to the environment. In contrast, renewable sources like solar energy offer cleaner alternatives but can be intermittent and require substantial upfront investment.
As we explore energy and sources of energy, the balance between demand and sustainability emerges as vital. Our choices impact not only our lives but also the planet's health. Addressing these challenges requires innovation and accountability. It prompts us to rethink our energy consumption and its broader implications, encouraging a more conscientious approach to energy use.

Importance of Energy in Modern Society
Energy plays a crucial role in modern society. It powers our homes, fuels vehicles, and drives industries. Without energy, daily activities would come to a halt. Think about it: you wake up to an electric alarm clock. You brew coffee and turn on lights, all thanks to energy.
Tip: Consider how you use energy daily. Small changes can make a significant impact.
The demand for energy continues to grow. Cities expand, and populations rise. Renewable energy sources like wind and solar are essential for sustainability. However, we also rely on fossil fuels. This dependence raises environmental concerns. It’s a complex situation that needs attention.
Tip: Evaluate your energy consumption. Simple actions, like turning off unused devices, can help.
We often take energy for granted. It’s easy to overlook its importance. Yet, the conversation about energy should be ongoing. We must balance our needs with environmental responsibility. Society must adapt to ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.
Impact of Energy on Economic Development
Energy is a cornerstone of economic development. It powers industries, facilitates transportation, and supports infrastructure. Without reliable energy sources, societies struggle to grow and innovate. Countries that prioritize energy access often see significant improvements in standards of living. Unfortunately, many regions still lack this essential resource.
The impact of energy on jobs is also profound. Energy-intensive sectors create millions of jobs. For example, construction, manufacturing, and services all depend heavily on energy. However, shifts in energy sources can disrupt job markets. Communities may find themselves unprepared for change, leading to economic instability.
Tips: Always stay informed about local energy policies. Understanding these can help businesses adapt. Consider energy efficiency solutions to save costs. Investing in renewable sources can foster long-term growth. This shift, albeit challenging, is essential for sustainable development. Embracing new energy technologies can spark innovative job opportunities. Reflect on how energy choices impact your community. Sometimes, the path forward isn't clear, but collective action can lead to meaningful improvements.
Why is Energy Important and What are its Sources? - Impact of Energy on Economic Development
| Energy Source | Description | Impact on Economic Development | Sustainability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Energy | Harnessing sunlight through solar panels. | Creates jobs in manufacturing and installation, reduces energy costs. | Highly sustainable; abundant and renewable. |
| Wind Energy | Utilizing wind turbines to generate electricity. | Promotes local investment and development; low operational costs. | Sustainable and excessive in windy regions. |
| Hydropower | Generating electricity from flowing water. | Ensures energy security and stability; can boost agriculture through irrigation. | Dependent on water quality and quantity; may impact local ecosystems. |
| Natural Gas | A fossil fuel used for heating, electricity, and as a fuel source. | Widely available; can drive down fuel costs, stimulate infrastructure growth. | Cleaner than coal but still a finite resource. |
| Biomass | Organic materials used as fuel, like wood, agricultural crops. | Provides energy and can reduce waste; supports rural economies. | Renewable but must be managed to prevent deforestation. |
Major Sources of Energy: Fossil Fuels, Renewables, and Nuclear
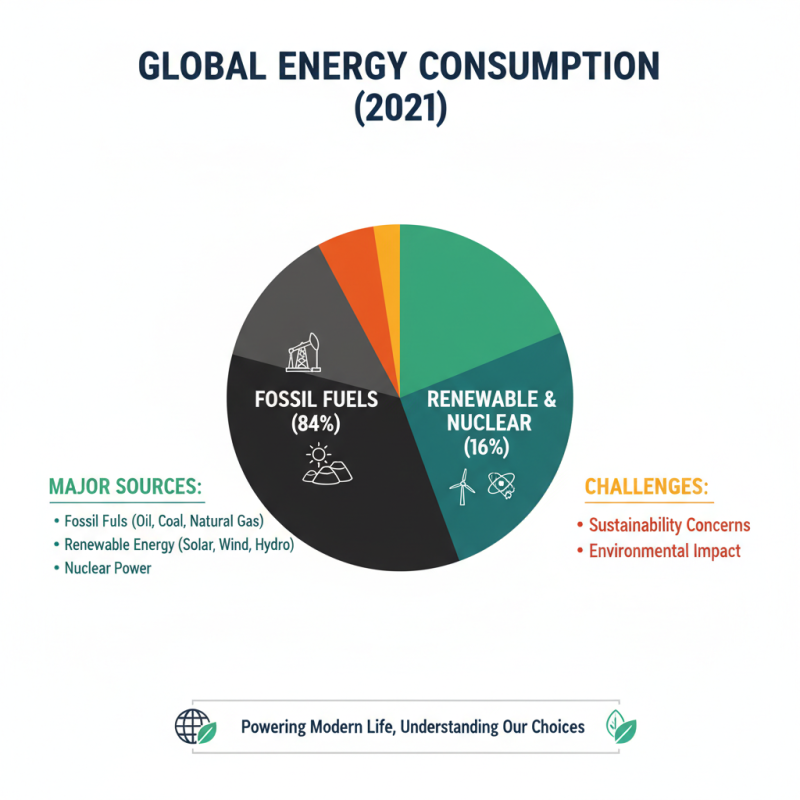
Energy is a vital component of modern life. It powers homes, industries, and transportation. Understanding its sources helps us appreciate its significance. Major sources of energy include fossil fuels, renewable energy, and nuclear power. In 2021, fossil fuels contributed to about 84% of global energy consumption. This reliance on oil, coal, and natural gas raises concerns about sustainability and environmental impact.
Renewable energy sources are gaining momentum. In 2020, they accounted for roughly 29% of global energy generation. Wind, solar, and hydroelectric power are key players in this category. The International Energy Agency (IEA) noted that renewables could provide over 70% of the world’s electricity by 2050 if investments continue. Yet, challenges remain. Storage solutions and grid integration need improvement to handle intermittent supply.
Tip: Explore local renewable energy programs. They can lower your utility bills and reduce your carbon footprint.
Nuclear power is another significant player, providing about 10% of global energy. Safety concerns and waste disposal issues are ongoing debates. Besides, nuclear energy has a smaller carbon footprint than fossil fuels. However, public perception can hinder its growth.
Tip: Educate yourself about energy sources. Knowledge drives better choices for the environment and energy consumption.
Comparing Renewable Energy Sources: Advantages and Challenges
Renewable energy sources are becoming increasingly significant. They offer benefits like sustainability and reduced emissions. Solar power harnesses sunlight, while wind energy relies on gusts. Both are clean, yet face challenges. Solar panels need ample space and sunlight. Wind turbines require consistent winds, which aren't available everywhere.
Hydropower is another option. It generates energy by using flowing water. However, building dams can disrupt local ecosystems. There’s also biomass, which utilizes organic materials. While it can reduce waste, its production can lead to deforestation.
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s internal heat. This method is reliable but limited to specific geographic areas. Each source has its pros and cons. That complexity can make energy choices feel overwhelming. Awareness of local resources and conditions is essential for effective energy planning.
Comparison of Renewable Energy Sources: Advantages and Challenges
This chart compares four major renewable energy sources based on their advantages and challenges. The data includes the average potential output and common challenges faced by each type.
Future Trends in Energy Production and Consumption
The future of energy production and consumption is transforming rapidly. Renewable energy sources are becoming dominant. According to a 2023 report by the International Energy Agency, renewables could supply 90% of global electricity by 2050. Solar and wind are leading this shift. However, challenges remain in storage technology. The need for efficient batteries is critical.
Energy consumption trends show increased demand for cleaner options. Many countries are setting ambitious goals for carbon neutrality. For instance, the global investment in renewables reached $500 billion last year. This investment reflects a shift in public and corporate priorities. Simultaneously, fossil fuel reliance is still an issue, especially in emerging markets. These regions struggle with balancing growth and sustainability.
Balancing traditional energy sources with new technologies is complex. Many industries are still heavily invested in non-renewable resources. Transitioning can be slow and painful. A clear path is necessary but not always available. As we innovate, some countries may lag behind. The equity in energy access remains a pressing question. The divide between developed and developing nations highlights ongoing struggles.
Related Posts
-

Unlocking the Future: Innovative Energy Solutions and Sustainable Sources for Tomorrow
-

Top 10 Sources of Energy: Which Are the Most Sustainable and Efficient?
-

Top 10 Benefits of Alternative Energy for a Sustainable Future
-

Exploring Alternative Energy Innovations at the 138th Canton Fair 2025: A Data-Driven Insight
-

Exploring Sustainable Energy Innovations at 2025 China 138th Canton Fair
-

What is Energy Solutions and How They Impact Global Sustainability Efforts

