How to Harness Technology and Energy for Sustainable Solutions?
In an era where climate change looms large, harnessing technology and energy is critical. Dr. Jane Smith, a leading expert in sustainable innovations, once stated, “The future depends on our ability to merge technology and energy sustainably.” Her words highlight the necessity of integrating these sectors.
Modern solutions are emerging at the intersection of technology and energy. For example, solar panels now generate power more efficiently than ever. Wind turbines are being equipped with smart technology to optimize energy production. These advancements are impressive but often come with challenges. The reliance on rare materials raises questions about sustainability.
As we pursue sustainable solutions, we must also reflect on our choices. Are we pushing technology too hard? Is our dependence on energy altering nature? These questions are vital as we navigate the complexities of technology and energy. The pathway to a sustainable future is not straightforward. It requires thoughtful consideration and collaboration across various fields.

Understanding the Interconnection Between Technology and Energy in Sustainability

Sustainability relies heavily on the synergy between technology and energy. Today, we see rapid advancements in renewable energy. Solar panels, wind turbines, and energy-efficient solutions are at the forefront. They transform how we produce and use energy. However, the integration of these technologies is not always seamless.
Many regions still face challenges in energy accessibility. Not every community has ready access to renewable sources. This inconsistency can hinder progress toward sustainability. Furthermore, while technology often promises efficiency, it can also lead to excess waste in production. The digital divide remains an issue as well. Some populations might not be equipped to embrace smart technology, leaving them behind in this green transition.
We must consider these complexities deeply. Harnessing technology for sustainability is not just about deployment; it’s about inclusivity. For true progress, we need diverse voices in the conversation. The journey toward a sustainable future is filled with obstacles. However, understanding the interplay between technology and energy is crucial. It pushes us to reflect and innovate continuously.
Exploring Renewable Energy Sources as a Core Component of Solutions
Renewable energy sources are essential for creating sustainable solutions. Solar, wind, and hydropower play key roles. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it to electricity. Wind turbines harness wind to generate power. These methods reduce reliance on fossil fuels. They also lower greenhouse gas emissions, a crucial step for the environment.
However, there are challenges. For instance, storage technology is still developing. Energy produced on windy or sunny days may not be usable later. This inconsistency can lead to energy shortages. We need better battery technology to address this issue. Moreover, transitioning to renewable sources requires investment. Many regions lack the infrastructure.
People often overlook the importance of community engagement. Local input can shape effective energy solutions. It’s vital to educate communities about using renewable options. Misunderstandings about renewable energy can hinder progress. Open conversations can lead to collaboration. Fostering an inclusive approach may encourage acceptance and innovation in clean energy initiatives.
Innovative Technologies Driving Energy Efficiency in Various Sectors
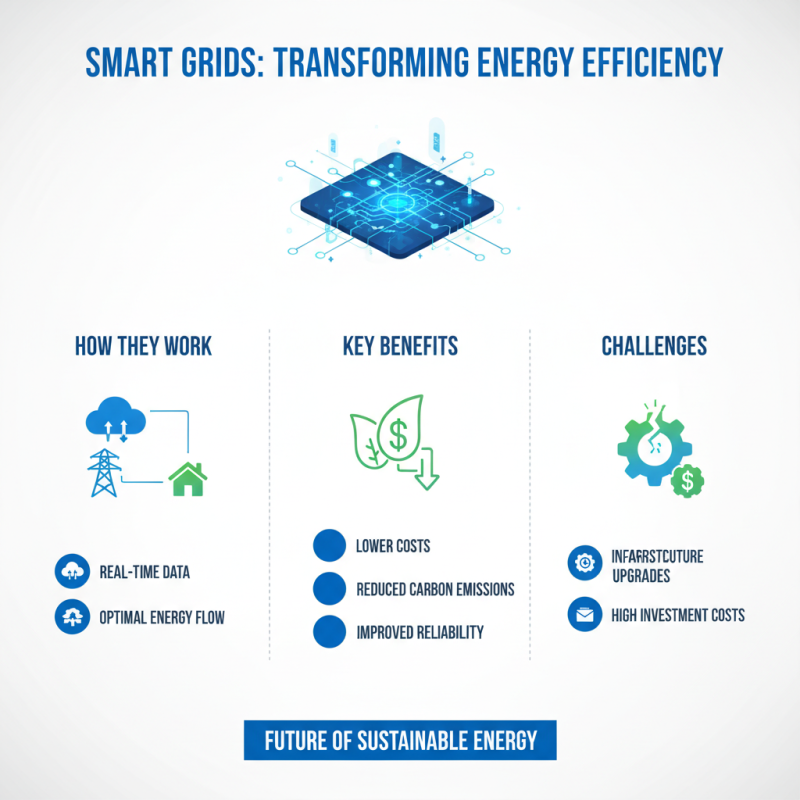
Innovative technologies are transforming energy efficiency across various sectors. Smart grids, for example, enhance energy distribution and minimize waste. They use real-time data to adjust energy flow, ensuring optimal usage. This not only reduces costs but also lowers carbon emissions. However, the transition to smart grids isn't seamless. Infrastructure challenges and investment costs can be significant.
In manufacturing, automation and IoT technologies are optimizing energy consumption. Machines communicate with each other, adjusting power usage based on demand. This proactive approach leads to substantial energy savings. Yet, reliance on technology raises concerns about cybersecurity and data privacy. Companies must address these issues to prevent potential breaches.
Building management systems also play a critical role. These systems monitor and control lighting, heating, and cooling efficiently. By analyzing usage patterns, they can suggest energy-saving adjustments. Still, there can be resistance to change from staff accustomed to traditional systems. Engaging employees in these processes can improve adoption and realization of benefits. Integrating innovative technologies into everyday practices requires ongoing effort and focus.
Implementing Smart Grid Systems for Enhanced Energy Management
The implementation of smart grid systems is crucial for improving energy management. Smart grids integrate digital technology and communication systems. These tools help monitor and control energy usage in real time. For example, homes can connect appliances to the grid, allowing for automatic adjustments based on energy demand. This flexibility can lead to energy savings and reduced costs.
Yet, there are challenges with smart grid adoption. Not all regions have the infrastructure needed to support such technologies. Some communities may lack access to reliable internet or advanced data processing systems. There may also be privacy concerns regarding data collection and usage. Educating the public about these technologies can be difficult.
Despite these obstacles, the potential benefits are significant. Improved energy distribution can reduce waste and lower emissions. Enhanced predictive capabilities can help manage the load more effectively. However, the transition requires careful planning and investment. Stakeholders must collaborate to ensure equitable access and robust technology. Continuous reflection on these issues is necessary for successful implementation.
How to Harness Technology and Energy for Sustainable Solutions? - Implementing Smart Grid Systems for Enhanced Energy Management
| Aspect | Description | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Meters | Devices that record electricity consumption in real-time. | Enhanced billing accuracy, increased consumer awareness. | Integration costs, consumer resistance. |
| Demand Response | Adjusting power usage by consumers during peak hours. | Reduced energy costs, improved grid reliability. | Technology limitations, participation challenges. |
| Renewable Integration | Incorporating solar and wind energy into the grid. | Lower carbon emissions, energy diversification. | Intermittency issues, infrastructure upgrades. |
| Energy Storage | Systems for storing energy for later use (e.g., batteries). | Grid stability, peak shaving. | High costs, environmental concerns. |
| Grid Modernization | Upgrading infrastructure to support advanced technologies. | Enhanced efficiency, reduced outages. | Funding requirements, regulatory challenges. |
Case Studies of Successful Sustainable Technology Initiatives Globally
Around the world, various successful sustainable technology initiatives have emerged. In a village in Africa,
solar-powered water pumps transformed access to fresh water. This technology reduced reliance on fuel generators, but it also faced maintenance issues.
Local communities needed training to handle repairs, which was sometimes overlooked.
In Asia, a project implemented a waste-to-energy system. Organic waste is converted into biogas for cooking and electricity.
While this initiative improved energy access, challenges arose in sourcing enough organic materials. Some communities struggled with inconsistent supply,
limiting the system's potential.
In Europe, urban gardening initiatives utilize technology for smart irrigation. Sensors measure soil moisture, optimizing water use. However, many
residents struggle with understanding the technology. Workshops are essential, but attendance can be low.
Addressing the knowledge gap is crucial for maximizing these innovative solutions. Each project shows progress, yet the need for ongoing adaptation and education remains.
Related Posts
-

Exploring Sustainable Energy Innovations at 2025 China 138th Canton Fair
-

What is Environmental Energy and How Does it Impact Our Future
-
Technology and Energy Tips for Sustainable Solutions?
-

Wind Farm Energy Innovations at 2025 China Import and Export Fair: Harnessing a $1 Trillion Industry
-

Harnessing Wind Energy for a Sustainable Future Beyond Fossil Fuels
-

Harnessing Power Energy for a Sustainable Future The Role of Renewable Sources in Global Energy Consumption

